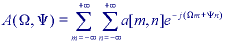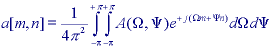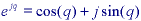







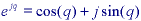
where
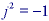 ,
we can say that the Fourier transform produces a representation of a (2D)
signal as a weighted sum of sines and cosines. The defining formulas for the
forward Fourier and the inverse Fourier transforms are as follows. Given an
image a and its Fourier transform A, then the forward transform
goes from the spatial domain (either continuous or discrete) to the frequency
domain which is always continuous.
,
we can say that the Fourier transform produces a representation of a (2D)
signal as a weighted sum of sines and cosines. The defining formulas for the
forward Fourier and the inverse Fourier transforms are as follows. Given an
image a and its Fourier transform A, then the forward transform
goes from the spatial domain (either continuous or discrete) to the frequency
domain which is always continuous.
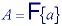
The inverse Fourier transform goes from the frequency domain back to the spatial domain.
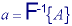
The Fourier transform is a unique and invertible operation so that:

The specific formulas for transforming back and forth between the spatial domain and the frequency domain are given below.
In 2D continuous space:
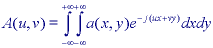
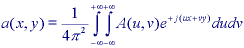
In 2D discrete space: