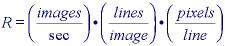







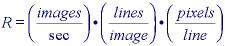
While the appropriate unit for describing the readout rate should be pixels / second, the term z is frequently found in the literature and in camera specifications; we shall therefore use the latter unit. For a video camera with square pixels (see Section 7.5), this means:
Format
|
lines
/ sec
|
pixels
/ line
|
R
(Mz.)
|
| NTSC
|
15,750
|
(4/3)*525
|
~11.0
|
| PAL
/ SECAM
|
15,625
|
(4/3)*625
|
~13.0
|
Note that the values in Table 12 are approximate. Exact values for square-pixel systems require exact knowledge of the way the video digitizer (frame grabber) samples each video line.
The readout rates used in video cameras frequently means that the electronic
noise described in Section 6.3 occurs in the region of the noise spectrum (eq.
) described by  >
>  max where the
noise power increases with increasing frequency. Readout noise can thus be
significant in video cameras.
max where the
noise power increases with increasing frequency. Readout noise can thus be
significant in video cameras.
Scientific cameras frequently use a slower readout rate in order to reduce the readout noise. Typical values of readout rate for scientific cameras, such as those described in Tables 9, 10, and 11, are 20 kz, 500 kz, and 1 Mz to 8 Mz.
